Are slow download speeds making it impossible to download files, games, and videos? Whether you’re downloading torrents or files through a web browser like Chrome, there are several straightforward adjustments you can make to significantly increase your download speeds. This guide will walk you through effective techniques to boost download speeds on a Windows PC or Mac, including tweaks to optimize your Wi-Fi or wired internet connection.
How to Make Downloads Go Faster
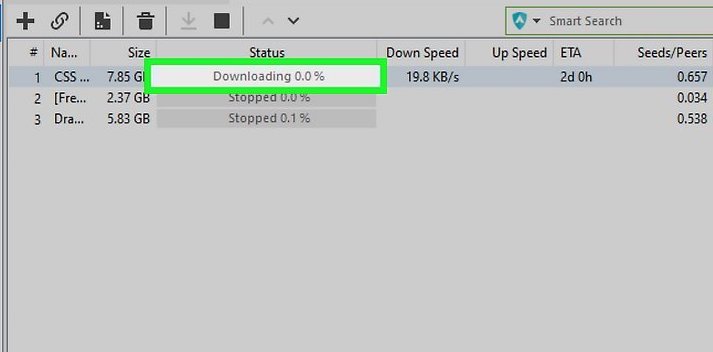
Stick to One Download at a Time
The more files you download simultaneously, the slower each file will progress. Limit your downloads to one file at a time to ensure maximum speed for each download.
Avoid Streaming Video and Music While Downloading
Streaming services such as Netflix, Hulu, Spotify, smart TV apps, and YouTube can significantly reduce your download speeds. Turn off all streaming activities while downloading large files.
- If others on your network are streaming content, this will also impact your download speeds. Ask your household members to pause their streaming while you complete your downloads.
Close Other Open Apps While Downloading
Having multiple applications and browser tabs open can significantly reduce your download speeds. Close any programs you are not actively using to free up bandwidth. Applications may consume bandwidth in the background even if they do not appear to be internet-intensive.
- For instance, if you’re downloading a game with BitTorrent, closing your web browser can help speed up the download.
Avoid Seeding or Uploading While Downloading Torrents
Seeding or uploading while downloading can severely limit your download speeds. It is more efficient to wait until all downloads are complete before starting to seed, preferably when you are not actively using the internet.
Enable Parallel Downloading
Parallel downloading establishes multiple connections to download different parts of a file simultaneously, increasing the overall download speed. Browsers such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, and Firefox support this feature.
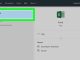
- Open Google Chrome, type
chrome://flagsin the address bar, and press Enter. - Search for “parallel” to quickly locate the parallel downloading option.
- Change the status from Default to Enabled and relaunch Chrome for the changes to take effect.
Perform an Internet Speed Test
Check your download speed by typing “internet speed” into Google and clicking the “RUN SPEED TEST” button. This will provide an estimate of your current download speed.
- If your actual download speed is significantly slower than the test result, the problem likely lies within your computer or local network, not your internet connection. Conversely, if the speed test reports a slow connection, there may be issues with your ISP, modem, router, or home wiring.
Restart Your Computer
A simple reboot of your PC or Mac can resolve issues affecting download speeds. Once your computer restarts, try downloading the file again for a potential speed boost.
Disconnect Other Devices From Your Network
Reduce the number of devices connected to your network. The more devices connected, the slower your internet speed. Disconnect any non-essential devices such as gaming consoles, smart TVs, phones, tablets, and additional computers.
Disable Background Apps
Background applications can consume bandwidth even if they do not display open windows. Disabling these apps can free up bandwidth for your downloads.
- Windows 10 & 11:
- Open Task Manager by pressing
Ctrl + Shift + Esc. - In the Processes tab, check the list of apps under “Background processes”.
- Select a task and click End Task to stop it.
- Open Task Manager by pressing
- Mac:
- In Finder, open the Applications folder, then Utilities, and double-click Activity Monitor.
- Select a process and click the X at the top-left corner to stop it.
- Click Quit to close the app safely, or Force Quit to close it immediately.
Get Closer to Your Wi-Fi Access Point
Wi-Fi signals weaken with distance. If your computer is far from the wireless router, move closer to improve download speeds. Using a wireless range extender can boost the signal to areas with weak coverage.
Switch Wi-Fi Frequencies
Switching between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies can benefit your download speeds based on your environment.
- 2.4 GHz: Provides wider coverage at slower speeds, suitable for long distances.
- 5 GHz: Offers faster speeds at shorter ranges, ideal for close proximity to the router.
- Physical obstructions and electronic interference can affect Wi-Fi performance. Minimize these to improve speeds.
Use Different DNS Servers
Your ISP’s default DNS servers might be slowing down your downloads. If the DNS servers used by your ISP are far away or overloaded, your internet speeds might suffer. Fortunately, there are reliable public DNS servers known for their speed and reliability, such as Google Public DNS and OpenDNS.
Google Public DNS:
- IPv4: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4
- IPv6: 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844
OpenDNS:
- IPv4: 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220
Change DNS Settings on Windows:
- Open Control Panel and select Network and Internet.
- Click Network and Sharing Center.
- Click Change adapter settings.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi or Ethernet interface and choose Properties.
- On the Networking tab, select TCP/IPv4 or TCP/IPv6, depending on your connection.
- Click Properties, then Advanced.
- Select “Use the following DNS server addresses,” enter the two addresses for your protocol, and then click OK and Apply.
Change DNS Settings on a Mac:
- Click the Apple menu, select System Settings (Ventura and later) or System Preferences (Monterey and earlier).
- Click Network.
- Select your connection and click Details.
- Click DNS.
- Click + and enter the first IPv4 or IPv6 server address. Then, click + again to enter the second IP address.
- Click OK.
Make Sure There Aren’t Any Updates Running
If operating system updates are running in the background, your downloads will slow to a crawl. Wait until updates are finished downloading and installing before downloading files. To check for active updates on your PC or Mac:
Windows:
- In the Start menu, select Settings, then choose Windows Update (Windows 11) or Update & Security > Windows Update (Windows 10).
- If an update is downloading, you’ll see its progress.
- You can select Pause to temporarily stop updates so you can finish your download.
Mac:
- macOS Ventura and later: Click the Apple menu, choose System Settings, select General, and then choose Software Update.
- macOS Monterey and earlier: Click the Apple menu, click System Preferences…, and select Software Update.
- If an update is installing, you’ll see its progress. It’s best to pause your download, finish your update, and then restart the download.
- To customize when your Mac downloads updates, click Advanced… and make your selections.
Set Bandwidth Limits for Background Downloads (Windows)
If Windows updates frequently bog down your downloads, you can limit the bandwidth used for updates. This can be easily adjusted in your Windows Update settings:
Windows 10:
- Open Start > Settings > Update & Security > Advanced Options > Delivery Optimization > Advanced options.
- Check the box next to “Limit how much bandwidth is used for downloading updates in the background,” and move the slider to the left to decrease update bandwidth.
Windows 11:
- Open Start > Settings > Windows Update > Advanced options > Delivery Optimization > Advanced options.
- Select “Absolute bandwidth,” check the box next to “Limit how much bandwidth is used for downloading updates in the background,” and enter a number in Mbps, such as “1.”
Clear Your Web Browser Cache
Having a hefty web browser cache can slow down web browsing, which can affect your downloads. No matter which web browser you’re using, clearing your browser cache can give you a quick speed boost.
Scan for Viruses and Malware
If your computer is infected with adware, spyware, a virus, or other malware, you’ll usually notice slower download speeds. Fortunately, you can run an antimalware scan for free. If you’re using Windows, use the built-in Microsoft Defender tool to run a scan. If you have a Mac, run a free scan using Avast or Malwarebytes.
Disable Metered Connection (Windows)
If your connection is metered (limited) to conserve bandwidth, your downloads will be slow. Metered connections are usually used when your internet service plan doesn’t include unlimited data. Just keep in mind that data overages may apply if you go over your allotted data plan.
- Click the Start menu and select Settings.
- Click Network & Internet and choose Wi-Fi (if using Wi-Fi) or Ethernet (for a wired connection).
- Click the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.
- Click Properties.
- Toggle off the “Set as metered connection” switch.
Delete Temporary Files (Windows)
Temporary files created by Windows may be slowing down your computer. If your PC is performing slowly, your downloads will be slow as well. Clearing your temporary files is quick, easy, and won’t affect your personal data.
- Type disk cleanup in the search bar, then click Disk Cleanup in the search results.
- Choose your hard drive and click OK.
- Click Clean up system files.
- Select your hard drive again and click OK.
- Check the boxes next to any files you want to delete, including Temporary files, Windows upgrade log files, and System recovery log files.
- Click OK and then Delete Files.
Restart Your Network
A quick network reset can clear up various issues, including slow download speeds.
- If you have a combination modem/router, unplug its power cord, remove any connected cables, and leave it unplugged for about 30 seconds. Reconnect the cables and turn the modem/router back on.
- If your modem and router are separate, unplug both power cords, and unplug the network cable that connects your modem to the wall outlet. Leave everything unplugged for 30 seconds, then reconnect your devices.
Switch to a Wired Connection
Connecting your computer to your router via Ethernet can provide a significant speed boost if you’re experiencing slow downloads over Wi-Fi. A wired connection often offers more stable and faster speeds.
Try a Different Web Browser
If you’re downloading files from a website, your current browser may not be optimized. If you’re using Safari on a Mac, try installing Chrome to see if you get better download speeds. If you normally use Chrome on your Windows PC, try using Microsoft Edge. You can also try alternative browsers like Brave or Opera.
Consider a Download Manager
If you download many files, a download manager can help you prioritize them. Download managers can accelerate downloads based on available connections and restart interrupted downloads.
- Internet Download Manager (IDM) is a popular tool for Windows that promises to speed up your downloads. IDM offers a 30-day free trial.
- Free Download Manager is a free, open-source option for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Update Your Router’s Firmware
If your router is running outdated firmware, you might be missing out on performance improvements. Router manufacturers often release updates that enhance connectivity and security. Check for and install the latest firmware updates for your router.
Consider a New Router
Older routers might not support the maximum speeds provided by your ISP. If your router is more than a couple of years old, it may not fully utilize your internet package’s speeds.
- If you lease a router from your ISP, contact them to inquire about newer models.
- When purchasing a new router, choose one that supports the same or higher download speeds as your internet package.
Upgrade Your Internet Connection
Some internet connections may not be capable of handling large downloads efficiently. Consider upgrading to a higher-tier plan offered by your ISP, such as “Gamer” or “Streamer” packages that prioritize download speeds.
Try Downloading from Another Source
Sometimes the issue lies with the source server or website. If one site or service is particularly slow, try downloading the file from a different source or wait for the service to resolve its network issues.

Add comment